Nitriding
Description
If you need hardening technologies and want to perform steel nitriding in Ukraine, then our company “Karbaz” will offer you this service at a favorable price.
Steel nitriding or diffuse enrichment of metal with nitrogen is a technology according to which parts are kept in nitrogen-containing gases or dissociated ammonia at a temperature above 500 degrees Celsius. As a result of this procedure, the core of the part receives a sorbite structure and acquires a surface layer.
The main goals of nitriding are: imparting hardness and strength, increasing wear resistance, improving the anti-corrosion properties of the metal.
Most often, various metal parts are subjected to nitriding:
– shafts and studs;
– rods and flanges;
– gears and rings.
It should be noted that these parts can have a diameter of up to 900 mm and a length of up to 1500 mm, so they must be processed on special equipment. Our company can perform simultaneous nitriding of parts weighing up to 100 kilograms. Nitriding is performed in electric furnaces with a steel muffle inside, heated ammonia is supplied to these furnaces.
Steel nitriding can help to achieve higher strength than the cementation procedure. After nitriding, parts can be heated to 500-600 degrees, while after cementation only 250 degrees Celsius. The strength properties of steel that has undergone the nitriding procedure are 1.5-2 times higher than after cementation or hardening.
The nitriding process is quite in demand and it should be noted that the price for steel nitriding in our company is quite affordable for enterprises of all types of ownership. Leave a request on the website and our manager will contact you as soon as possible.
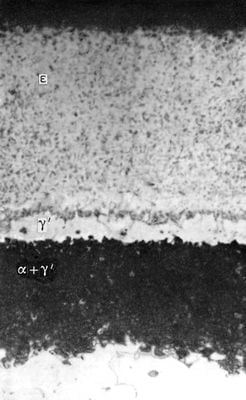
After nitriding, the core of the part has a sorbite structure obtained by heat treatment before the nitriding process, and the surface layer with a thickness of 0.01-0.6 mm (depending on the purpose) has a microstructure shown in the figure below.
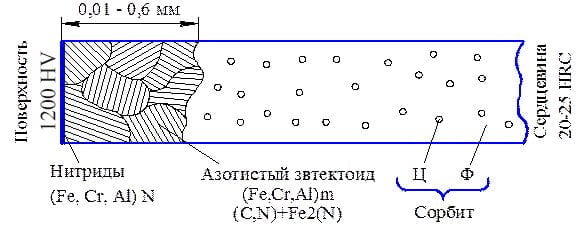
OUR NITRIDING CAPABILITIES
Dimensions of workpieces:
- - rings, gear wheels, flanges, etc. with a diameter of up to 900 mm;
- - shafts, rods, studs, etc. up to 1500 mm long;
- Weight of processed parts – up to 100 kg
Dimensions of workpieces:
- - rings, gear wheels, flanges, etc. with a diameter of up to 900 mm;
- - shafts, rods, studs, etc. up to 1500 mm long;
- Weight of processed parts – up to 100 kg
PURPOSE OF NITRIDING
Saturation of iron alloys with nitrogen changes the state of the structure and thereby increases:
- static and dynamic strength,
- hardness
- wear resistance
- corrosion properties of these materials.
Nitriding allows to obtain more stable steel hardness indicators than when performing carburizing. Thus, the surface layer of a product that has been nitrided retains its hardness even when heated to a temperature of 550–600°, while after carburizing the hardness of the surface layer may begin to decrease already when the product is heated above 225°. The strength characteristics of the surface layer of steel after nitriding are 1.5–2 times higher than after hardening or carburizing.
Since the processing temperature does not exceed 600°C, structural transformations similar to those that occur as a result of austenitization during quenching do not occur, which allows cooling at any rate without the risk of martensite. For this reason, unlike quenching, deformation and warping of nitrided parts and tools are insignificant. This makes it possible to simplify subsequent processing and even get rid of it altogether, i.e. to subject finished parts that have undergone machining and grinding to nitriding without an allowance for final processing as in case of carburizing.
Nitriding is carried out in special electric furnaces with a sealed steel muffle inside, where the parts are placed, and then ammonia NH3 is supplied, which dissociates (breaks down) into atomic nitrogen and hydrogen under the influence of temperature.
The nitrogen atoms embedded in the surface layer of the material subsequently diffuse both along the grain boundaries and through them.
The following stages are characteristic of the nitriding process:
- Nitrogen supply from the appropriate environment to the surface of the part;
- Formation of a boundary layer at the surface of the part, where dissociation of the nitrogen-containing environment and adsorption of nitrogen atoms by the surface occur at the interface between the medium and the metal;
- Penetration (absorption) of nitrogen atoms through the surface into the material of the part
- Diffusion of nitrogen atoms into the surface layer of the part along the grain boundaries and through the grains.
Low nitriding temperature does not allow for deep saturation of the surfaces. The nitriding rate is approximately 0.01 mm/h. Therefore, the usual thickness of the nitrided layer for structural steels is within 0.2 – 0.5 mm, and the duration of the process is 2-3 times longer than the duration of carburization.
MAIN STAGES OF MANUFACTURING PARTS SUBJECT TO NITRIDING
- Rough machining.
- Preliminary heat treatment of metal (the so-called thermal improvement), which includes two operations – hardening and tempering (high). Such treatment provides high viscosity and strength of the core of the part. Steel hardening is carried out at high temperatures (850-950˚С) with subsequent cooling in oil or water. Tempering temperature – from 600 to 670˚С.
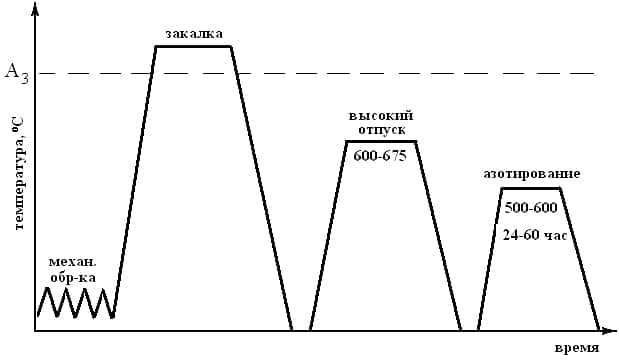
- Final machining of the part, incl.metal grinding. These operations are required to ensure that the part has the required (final) geometric parameters.
- Protection of parts of the metal surface that are not planned to be saturated with nitrogen. Liquid glass coating or tin coating is applied, which is applied to the workpiece with a thickness of no more than 0.015 millimeters using electrolytic technology.
- Direct saturation of the steel surface with nitrogen – nitriding.
- After all these procedures, finishing is performed , or grinding of parts
Metal nitriding
– is the process of treating the surface of a metal with nitrogen, which penetrates the metal surface, improving its mechanical properties. This process can significantly increase the hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the metal.
In the process of metal nitriding the metal surface is immersed in a special chamber where it is subjected to high temperatures and vacuum to create certain conditions for introducing nitrogen into the metal surface. Nitriding can be performed using either a nitrogen gas mixture or nitrogen salts in special solutions.
One of the main The advantages of metal nitriding are the improvement of its mechanical properties. In particular, nitriding increases the hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance of the metal. This makes it particularly useful for industries where metal products and parts are subject to intense wear and corrosion.
In addition, metal nitriding can also be used to improve its electrical properties, such as increasing electrical conductivity or reducing electrical resistance. This technology can also be used for improving the adhesion of coatings on metal surfaces.
In general, metal nitriding is an effective way to improve the mechanical and electrical properties of metal, making it useful for a variety of industries, including automotive, aviation, and medical.
